
SL Paper 3
Lanthanum, La, and antimony, Sb, form compounds with bromine that have similar formulas, LaBr3 and SbBr3.
Determine the type of bond present in SbBr3, showing your method. Use sections 8 and 29 of the data booklet.
Lanthanum has a similar electronegativity to group 2 metals. Explain, in terms of bonding and structure, why crystalline lanthanum bromide is brittle.
In order to determine the oil content of different types of potato crisps (chips), a student weighed of crushed crisps and mixed them with of non-polar solvent.
She assumed all the oil in the crisps dissolved in the solvent.
The student then filtered the mixture to remove any solids, and gently heated the solution on a hot plate to evaporate the solvent.
She measured the mass of the oil that remained from each type of crisps
Suggest why a non-polar solvent was needed.
State one reason why the mixture was not heated strongly.
Non-polar solvents can be toxic. Suggest a modification to the experiment which allows the evaporated solvent to be collected.
Suggest one source of error in the experiment, excluding faulty apparatus and human error, that would lead to the following:
The mild analgesic aspirin can be prepared in the laboratory from salicylic acid.
(CH3CO)2O + HOC6H4COOH → CH3CO2C6H4COOH + CH3COOH
Salicylic acid Aspirin
After the reaction is complete, the product is isolated, recrystallized, tested for purity and the experimental yield is measured. A student’s results in a single trial are as follows.
Literature melting point data: aspirin = 138–140 °C
Determine the percentage experimental yield of the product after recrystallization. The molar masses are as follows: M(salicylic acid) = 138.13 g mol−1, M(aspirin) = 180.17 g mol−1. (You do not need to process the uncertainties in the calculation.)
Suggest why isolation of the crude product involved the addition of ice-cold water.
Justify the conclusion that recrystallization increased the purity of the product, by reference to two differences between the melting point data of the crude and recrystallized products.
State why aspirin is described as a mild analgesic with reference to its site of action.
Polymers are made up of repeating monomer units which can be manipulated in various ways to give structures with desired properties.
(i) Draw the structure of 2-methylpropene.
(ii) Deduce the repeating unit of poly(2-methylpropene).
Deduce the percentage atom economy for polymerization of 2-methylpropene.
(i) Suggest why incomplete combustion of plastic, such as polyvinyl chloride, is common in industrial and house fires.
(ii) Phthalate plasticizers such as DEHP, shown below, are frequently used in polyvinyl chloride.
With reference to bonding, suggest a reason why many adults have measurable levels of phthalates in their bodies.
The table summarizes some properties of graphite and graphene.
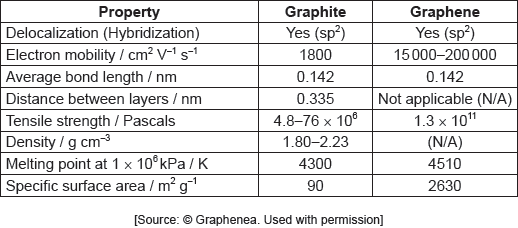
Graphene is two-dimensional, rather than three-dimensional, material.
Justify this by using the structure of graphene and information from the table.
Show that graphene is over 1600 times stronger than graphite.
Identify a value from the table which can be used to support the information about graphene given below.
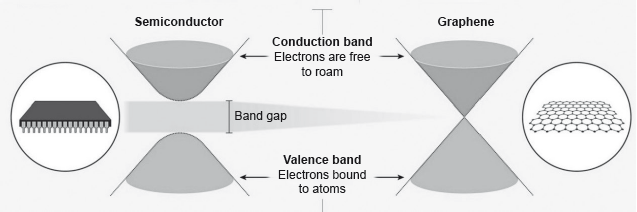
Electrons in a solid are restricted to certain ranges, or bands, of energy (vertical axis). In an insulator or semiconductor, an electron bound to an atom can break free only if it gets enough energy from heat or a passing photon to jump the “band gap”, but in graphene the gap is infinitely small.

Diamond, graphene, and graphite are all network solids.
Suggest, giving a reason, the electron mobility of diamond compared to graphene.
The melting point of diamond at 1 × 106 kPa is 4200 K (in the absence of oxygen).
Suggest, based on molecular structure, why graphene has a higher melting point under these conditions.
The structure of aspirin is shown in section 37 of the data booklet.
Suggest one reactant used to prepare aspirin from salicylic acid.
Aspirin, C6H4(OCOCH3)COOH, is only slightly soluble in water.
Outline, including an equation, how aspirin can be made more water-soluble. Use section 37 in the data booklet.
Lactose is a disaccharide formed by the condensation reaction of the monosaccharides galactose and glucose.
Describe what is meant by a condensation reaction.
Draw the structure of galactose on the skeleton provided.
Explain how the inclusion of carbohydrates in plastics makes them biodegradable.
Lipids are an important part of the human diet.
Fatty acids react with glycerol to form fats and oils. State the name of the chemical link formed in this reaction and the name of the other product.
The table below shows average figures for the percentage fatty acid composition of some common fats and oils.
(i) Deduce, with a reason, which fat or oil from the table above has the lowest iodine number.
(ii) Deduce, with a reason, which fat or oil from the table above is most likely to become rancid when exposed to the air.
(iii) The P/S index of a fat or oil is the ratio of polyunsaturated fat to saturated fat present. It is sometimes used to compare the relative health benefits of different lipids in the diet. Calculate the P/S index of beef fat and soybean oil.
(iv) Suggest why a P/S index of greater than 1 is considered beneficial to health.
(v) Cotton seed oil and corn oil have similar iodine numbers but the melting point of cotton seed oil is higher than that of corn oil. Suggest an explanation in terms of the structure and bonding in these two oils.
Proteins are polymers of amino acids. A paper chromatogram of two amino acids, A1 and A2, is obtained using a non-polar solvent.
© International Baccalaureate Organization 2020.
Determine the value of A1.
Proteins are polymers of amino acids.
The mixture is composed of glycine, , and isoleucine, . Their structures can be found in section 33 of the data booklet.
Deduce, referring to relative affinities and , the identity of A1.
Proteins are polymers of amino acids.
Glycine is one of the amino acids in the primary structure of hemoglobin.
State the type of bonding responsible for the α-helix in the secondary structure.
Proteins are polymers of amino acids.
Describe how the tertiary structure differs from the quaternary structure in hemoglobin.
Polypropene is used to make many objects including carpets, stationery and laboratory equipment.
Draw a section of an isotactic polypropene polymer chain containing four repeating units.
Predict, with a reason, whether isotactic or atactic polypropene has the higher melting point.
Polypropene is a thermoplastic. Outline what is meant by thermoplastic.
Discuss why the recycling of plastics is an energy intensive process.
Aspirin is formed by reacting salicylic acid with ethanoic anhydride. The structure of aspirin is given in section 37 of the data booklet.
Deduce the structural formula of the by-product of this reaction.
Aspirin crystals are rinsed with water after recrystallization to remove impurities.
Suggest why cold water is used.
The solubility of aspirin is increased by converting it to an ionic form. Draw the structure of the ionic form of aspirin.
Comment on the risk of overdose when taking aspirin as an analgesic, referring to the following values, for a person weighing :
Minimum therapeutic dose
Estimated minimum lethal dose
Solubility plays an important role in the bioavailability of drugs in the body.
Suggest why aspirin is slightly soluble in water. Refer to section 37 of the data booklet.
Formulate an equation for the conversion of aspirin to a more water soluble derivative.
A student prepares aspirin from salicylic acid in the laboratory, extracts it from the reaction mixture, ensures the sample is dry and determines its melting point.
Suggest why the melting point of the student’s sample is lower and not sharp compared to that of pure aspirin.
Organic molecules can be characterized using infrared (IR) spectroscopy.
Compare and contrast the infrared peaks above 1500 cm−1 in pure samples of aspirin and salicylic acid using section 26 of the data booklet.
The pharmaceutical industry is one of the largest producers of waste solvents.
State a green solution to the problem of organic solvent waste.
Palmitic acid has a molar mass of 256.5 g mol−1.
The apparatus in the diagram measures the surface pressure created by palmitic acid molecules on the surface of water. This pressure is caused by palmitic acid molecules colliding with the fixed barrier. The pressure increases as the area, A, available to the palmitic acid is reduced by the movable barrier.
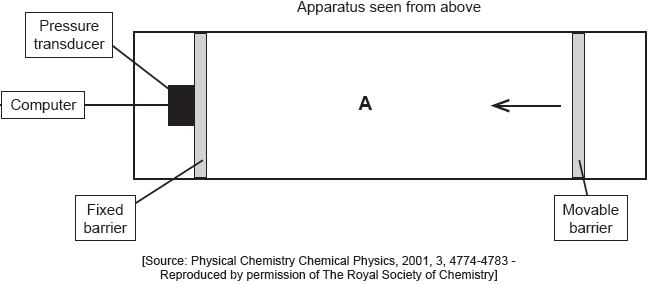
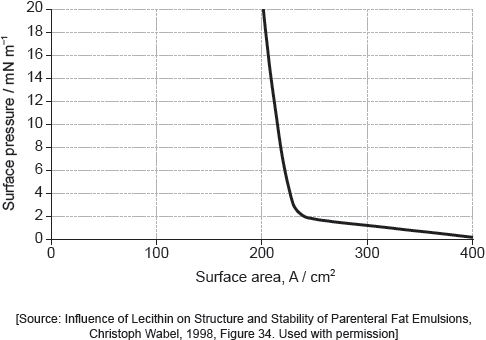
When a drop of a solution of palmitic acid in a volatile solvent is placed between the barriers, the solvent evaporates leaving a surface layer. The graph of pressure against area was obtained as the area A was reduced.
Part of this molecule is hydrophilic (bonds readily to water) and part hydrophobic (does not bond readily to water). Draw a circle around all of the hydrophilic part of the molecule.
When a small amount of palmitic acid is placed in water it disperses to form a layer on the surface that is only one molecule thick. Explain, in terms of intermolecular forces, why this occurs.
Suggest why there is a small increase in the surface pressure as the area is reduced to about 240 cm2, but a much faster increase when it is further reduced.
The solution of palmitic acid had a concentration of 0.0034 mol dm−3. Calculate the number of molecules of palmitic acid present in the 0.050 cm3 drop, using section 2 of the data booklet.
Assuming the sudden change in gradient occurs at 240 cm2, calculate the area, in cm2, that a single molecule of palmitic acid occupies on surface of the water.
If you did not obtain an answer for (b)(ii) use a value of 8.2 × 1016, but this is not the correct answer.
The development of materials with unique properties is critical to advances in industry.
Low density polyethene (LDPE) and high density polyethene (HDPE) are both addition polymers.
Outline two properties a substance should have to be used as liquid-crystal in a liquid-crystal display.
Describe how the structures of LDPE and HDPE affect one mechanical property of the plastics.
One of the two infrared (IR) spectra is that of polyethene and the other of polytetrafluoroethene (PTFE).
Deduce, with a reason, which spectrum is that of PTFE. Infrared data is given in section 26 of the data booklet.
Many plastics used to be incinerated. Deduce an equation for the complete combustion of two repeating units of PVC, (–C2H3Cl–)2.
Sunflower oil contains stearic, oleic and linoleic fatty acids. The structural formulas of these acids are given in section 34 of the data booklet.
Explain which one of these fatty acids has the highest boiling point.
10.0 g of sunflower oil reacts completely with 123 cm3 of 0.500 moldm–3 iodine solution. Calculate the iodine number of sunflower oil to the nearest whole number.
Suggest, in terms of its structure, why vitamin D is fat-soluble using section 35 of the data booklet.
There has been significant growth in the use of carbon nanotubes, CNT.
Explain these properties of carbon nanotubes.
Alloying metals changes their properties. Suggest one property of magnesium that could be improved by making a magnesium–CNT alloy.
Pure magnesium needed for making alloys can be obtained by electrolysis of molten magnesium chloride.
© International Baccalaureate Organization 2020.
Write the half-equations for the reactions occurring in this electrolysis.
Calculate the theoretical mass of magnesium obtained if a current of is used for hours. Use charge and section 2 of the data booklet
Suggest a gas which should be continuously passed over the molten magnesium in the electrolytic cell.
Zeolites can be used as catalysts in the manufacture of CNT. Explain, with reference to their structure, the high selectivity of zeolites.
Experiments have been done to explore the nematic liquid crystal behaviour of CNT. Justify how CNT molecules could be classified as nematic.
Peptidase enzyme in the digestive system hydrolyses peptide bonds.
A tripeptide Ala-Asp-Lys was hydrolysed and electrophoresis of the mixture of the amino acids was carried out at a pH of 6.0. Refer to section 33 of the data booklet.
Identify the type of metabolic process that occurs in the hydrolysis of the peptide during digestion.
Identify the name of the amino acid that does not move under the influence of the applied voltage.
Deduce, giving a reason, which amino acid will develop closest to the negative electrode.
The breakdown of a dipeptide in the presence of peptidase was investigated between 18 °C and 43 °C. The results are shown below.
Comment on the rate of reaction at temperature X in terms of the enzyme’s active site.
The solubility of a vitamin depends on its structure.
Identify the vitamin given in section 35 of the data booklet that is the most soluble in water.
Pollution from heavy metal ions has become a health concern.
Outline how the presence of heavy metal ions decreases the action of enzymes.
Outline how lead ions could be removed from an individual suffering from lead poisoning.
| Phospholipids are a main component of cell membranes. |
Deduce the products of the hydrolysis of a non-substituted phospholipid, where and represent long alkyl chains.
A representation of a phospholipid bilayer cell membrane is shown:
© International Baccalaureate Organization 2020.
Identify the components of the phospholipid labelled A and B.
State the most significant intermolecular forces in the phospholipid in b(i).
Phospholipids help maintain cellular environments while fatty acid lipids have important roles in energy storage and electrical insulation. Discuss the structural properties of saturated fats needed for these roles.
Materials science involves understanding the properties of materials and applying those properties to desired structures.
Magnesium oxide, MgO, and silicon carbide, SiC, are examples of ceramic materials. State the name of the predominant type of bonding in each material.
Predict the predominant type of bonding for a binary compound AB in which the electronegativity of both atoms is low. Use section 29 of the data booklet.
Vitamins are organic compounds essential in small amounts.
State the name of one functional group common to all three vitamins shown in section 35 of the data booklet.
Explain the biomagnification of the pesticide DDT.
Explain why maltose, C12H22O11, is soluble in water.
Infrared (IR) spectroscopy is often used for the identification of polymers, such as PETE, for recycling.
LDPE and high density polyethene (HDPE) have very similar IR spectra even though they have rather different structures and physical properties.
Below are the IR spectra of two plastics (A and B); one is PETE, the other is low density polyethene (LDPE).
Deduce, giving your reasons, the identity and resin identification code (RIC) of A and B using sections 26 and 30 of the data booklet.
Describe the difference in their structures.
Explain why the difference in their structures affects their melting points.
Lipids and carbohydrates contain the same elements but have different properties.
List the building blocks of triglycerides and carbohydrates.
The drain pipe of a kitchen sink can become clogged by fatty acids, such as linoleic acid, C18H32O2, but not by the trisaccharide, raffinose, C18H32O16, containing the same number of carbon atoms.
Explain why raffinose is far more water soluble than linoleic acid.
Solid fat triglycerides can also clog kitchen sink drains.
Explain how sodium hydroxide unblocks the drain.
The amount of proteins, fats and carbohydrates determine the energy content of foods.
Explain why linoleic acid, C18H32O2, is a more efficient energy storage molecule than raffinose, C18H32O16.
Metals are extracted from their ores by various means.
Aluminium is produced by the electrolysis of alumina (aluminium oxide) dissolved in cryolite.
Discuss why different methods of reduction are needed to extract metals.
Determine the percentage of ionic bonding in alumina using sections 8 and 29 of the data booklet.
Write half-equations for the electrolysis of molten alumina using graphite electrodes, deducing the state symbols of the products.
Anode (positive electrode):
Cathode (negative electrode):
The structures of morphine, diamorphine and codeine are given in section 37 of the data booklet.
Explain why diamorphine passes more readily than morphine through the blood-brain barrier.
Suggest a reagent used to prepare diamorphine from morphine.
Suggest one reason why codeine is available without prescription in some countries whilst morphine is administered under strict medical supervision.
Stearic acid (Mr = 284.47) and oleic acid (Mr = 282.46) have the same number of carbon atoms. The structures of both lipids are shown in section 34 of the data booklet.
The iodine number is the number of grams of iodine which reacts with 100 g of fat. Calculate the iodine number of oleic acid.
State one impact on health of the increase in LDL cholesterol concentration in blood.
Explain why stearic acid has a higher melting point than oleic acid.
State one similarity and one difference in composition between phospholipids and triglycerides.
Similarity:
Difference:
Identify a reagent that hydrolyses triglycerides.
Vitamins can be water-soluble or fat-soluble.
Explain, at the molecular level, why vitamin D is soluble in fats. Use section 35 of the data booklet.
State one function of vitamin D in the body.